That sinking feeling when Windows 11 misbehaves. Apps freeze, screens go blue, everything halts. Frustration builds fast. When Windows 11 crashes repeatedly, Windows 11 Safe Mode is your lifeline. Think of it as a stripped-down emergency version. It loads only bare essentials, bypassing extra software, drivers, and background apps. This minimal state helps untangle problems. Hunt malware hiding in normal mode, fix conflicts from bad drivers, undo breaking settings, tackle crashes or update failures. It gives you a chance to repair when the normal environment is unstable.
TL;DR: Quick Steps to Boot into Windows 11 Safe Mode
Short on time? Fastest way to Boot into Safe Mode Windows 11 if logged in:
- Open Settings > System > Recovery.
- Click “Restart now” under “Advanced startup.”
- Post-restart: Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Press F4 for basic Safe Mode or F5 for Windows 11 Safe Mode with Networking.
What is Windows 11 Safe Mode? (And Why You Need It)
Safe Mode is Windows 11 running on life support, focusing only on core functions.
How Safe Mode Works
Windows starts with blinders on. It ignores almost everything non-essential. Third-party apps? Skipped. Fancy drivers? Usually blocked. Non-critical services? On hold. Only fundamental drivers and services critical for basic operation load. This reduces complexity drastically. It creates a clean, stable environment where outside interference problems are less likely. You get a functional desktop, basic and slow. Trade-off for stability.
When to Use Safe Mode
Reach for Safe Mode when Windows 11 acts badly. Suspect resisting malware? Safe Mode often stops it from loading, letting tools clean it. Did a new driver cause crashes? Boot into Safe Mode to uninstall it safely. Frequent Blue Screens (BSODs), freezes, or instant app crashes? Safe Mode helps find if core files are damaged or a background process is guilty. Stuck by a failed Windows Update? Safe Mode provides stability to uninstall it or run repairs.
Safe Mode Variations Explained
Windows 11 offers three main flavors:
- Safe Mode (Press F4): Most basic. Minimal drivers/services. Offers Safe Mode without Internet Windows 11. No network access, safest for severe malware or network conflicts.
- Safe Mode with Networking (Press F5): Adds essential network drivers/services. Internet access. Use for downloads, online help, cloud backups.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt (Press F6): Boots directly into Command Prompt. For IT pros or command-savvy users. Run tools like sfc /scannow, DISM, chkdsk, malware scanners.
Prerequisites for Safe Mode
Prepare before diving in. Prevents headaches.
Backup Critical Data
Troubleshooting can be unpredictable. Protect important files. Use File History or OneDrive. Copy documents, photos, files to an external drive or cloud. Don’t skip this. Losing data adds stress.
Administrator Access Required
You need admin privileges. Most personal accounts are admins. If using a standard account, need an admin password. Trying without rights causes errors or blocks.
Power and Peripheral Checks
Ensure laptop is plugged in. Sudden shutdown during boot/repair can cause file corruption. Disconnect non-essential peripherals: printers, external drives (except backups), USB hubs, cameras, new hardware. Leave only keyboard, mouse, monitor. Eliminates conflicts.
5 Methods to Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode
Choose based on your situation.
Method 1: Via Settings App (Logged In)
Use this if you can sign into desktop.
- Press Win + I for Settings.
- Go System > Recovery.
- Click “Restart now” under “Advanced startup.”
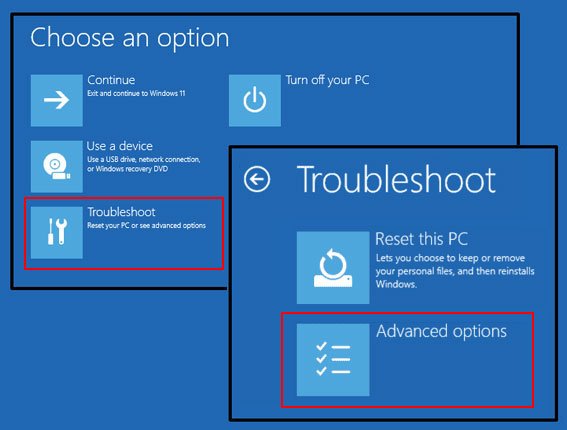
- PC reboots into Windows 11 Recovery Environment (blue “Choose an option”).
- Select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Press F4 to Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode, F5 for Networking, F6 for Safe Mode Command Prompt Windows 11.
Best For: When logged in normally. User-friendly.
Method 2: From Sign-in Screen (No Login)
Use if stuck at login due to crashes or lockouts (Safe Mode from Sign-in Screen).
- On sign-in screen, click Power icon (bottom right).
- Hold Shift key.
- While holding Shift, click “Restart.” Hold until recovery menu appears.
- PC restarts into blue menu (WinRE).
- Go Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Press F4, F5, or F6.
Best For: Can reach sign-in screen but can’t log in. Provides Access Safe Mode Windows 11.
Method 3: Using System Configuration (msconfig)
Forces next boot into Safe Mode. Use caution (Windows 11 Safe Mode msconfig).
- Press Win + R, type msconfig, press Enter.
- Go “Boot” tab.
- Check “Safe boot.”
- Select type: “Minimal” (F4), “Network” (F5), “Alternate shell” (F6).
- Click “Apply,” then “OK.”
- Restart when prompted.
WARNING: Sets persistent Safe Mode. Must undo post-repair! After fixing, reopen msconfig, uncheck “Safe boot,” Apply/OK, restart to Disable Safe Boot Windows 11. Forgetting causes Safe Mode Loop Fix.
Method 4: Via Command Prompt/PowerShell
Command-line configuration (Force Safe Mode Windows 11).
- Search “cmd” or “PowerShell” in Start.
- Right-click, “Run as administrator.”
- Type one command:
- bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal (Basic)
- bcdedit /set {default} safeboot network (Networking)
- Press Enter. Close window.
- Restart PC. Boots into chosen Safe Mode.
- To Exit: Reopen admin Command Prompt/PowerShell (in Safe Mode or normal), type: bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot, press Enter. Close. Restart to Exit Safe Mode Windows 11.
Best For: Command-line users, IT pros.
Method 5: Interrupt Boot Sequence (Advanced)
For critical boot failures (Windows 11 Automatic Repair Safe Mode).
- Turn on PC.
- At Windows logo, force shutdown via power button (5-10 sec).
- Turn PC on.
- At logo again, force shutdown.
- Turn PC on third time.
- After third interruption, launches Automatic Repair.
- Click “Advanced options.”
- Go Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Press F4, F5, or F6.
Best For: PC can’t load login screen. Last resort.
Exiting Safe Mode
Usually simple.
Standard Exit
- Click Start > Power icon.
- Select “Restart.”
PC restarts normally. Easiest way to Exit Safe Mode Windows 11.
If Stuck in a Loop
Used Method 3 or 4? Undo change from within Safe Mode:
- Msconfig: Open msconfig (Win + R > msconfig). Boot tab > Uncheck “Safe boot” > Apply/OK > Restart.
- Bcdedit: Open admin Command Prompt/PowerShell. Type bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot > Enter > Close > Restart. Essential Safe Mode Loop Fix.
Troubleshooting Safe Mode Issues
“Safe Mode Won’t Start” Fixes
If PC refuses entry or crashes:
- Recovery Media: Boot from Windows 11 USB installer > “Repair your computer.”
- BIOS/UEFI: Enter setup (Del/F2/F10/Esc). Ensure Secure Boot on, boot drive detected first. Troubleshoot Safe Mode Windows 11 externally.
Black Screen in Safe Mode
Only see black screen? (Windows 11 Safe Mode Black Screen):
- Graphics: Try different display port/monitor. Use Safe Mode with Networking (F5). Once in, roll back/update display driver via Device Manager (Safe Mode for Driver Issues).
- Hardware: Possible failing GPU, motherboard, RAM. Run manufacturer diagnostics.
Safe Mode with Networking Not Working
Chose F5 but no internet?
- Check cable/Wi-Fi connection (system tray icon).
- Reinstall Drivers: Device Manager > Network adapters > Right-click card > Uninstall device > Check “Delete driver” if shown > Uninstall > Restart PC normally > Let Windows reinstall drivers > Retry.
- System File Check: Admin CMD > sfc /scannow > Restart.
Advanced Safe Mode Scenarios
Using Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Powerful for text tools (Safe Mode Command Prompt Windows 11):
- sfc /scannow – Fixes system files.
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth – Repairs Windows image (better with Networking).
- chkdsk C: /f /r – Checks/fixes disk errors (restart needed).
- Run command-line malware scanners.
- rstrui.exe – Launches System Restore Safe Mode.
Safe Mode for Driver Updates/Rollbacks
Fix driver conflicts:
- Device Manager (Right-click Start).
- Find device with yellow mark (Display, Sound, Network, etc.).
- Roll Back: Right-click > Properties > Driver tab > Roll Back Driver (if available) > Restart.
- Uninstall: Right-click > Uninstall device > Check “Delete driver” > Uninstall > Restart normally > Windows installs basic driver > Manually download latest stable driver. Core Safe Mode for Driver Issues.
FAQs About Windows 11 Safe Mode
1. What’s the difference between Safe Mode and normal startup?
Normal startup loads everything: desktop, startup programs, drivers, apps, services. Safe Mode loads only minimum drivers/services needed for a basic desktop. Third-party items are skipped for stability during fixes.
2. Can I access the internet in Safe Mode?
Only if you choose “Safe Mode with Networking” (F5). Standard Safe Mode (F4) blocks internet access. Choose F5 for online help or downloads.
3. Why use Safe Mode with Command Prompt?
For advanced repairs using commands: sfc /scannow, chkdsk, DISM, malware tools, or starting System Restore (rstrui.exe). Needs command knowledge.
4. How do I know if I’m in Safe Mode?
“Safe Mode” text appears in all four screen corners. Desktop background is black. Resolution is low (e.g., 800×600). Looks basic.
5. Can I update drivers in Safe Mode?
Generally no. Windows Update doesn’t run. Installers often fail. Use Safe Mode to remove or roll back bad drivers. Update them normally after restarting.
6. What if Safe Mode doesn’t fix my problem?
If the issue persists or returns, try System Restore Safe Mode. Consider “Reset this PC” from WinRE. Reinstall Windows 11 as last resort.
7. Is Safe Mode safe for hardware?
Yes. It’s a software configuration change. Doesn’t alter hardware settings or pose physical risks. Reduces software load for safer fixes.
8. Why does my PC keep booting into Windows 11 Safe Mode?
Persistent Safe Mode is likely enabled via msconfig or bcdedit. Disable Safe Boot Windows 11 using the same method: Uncheck in msconfig or run bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot then restart.